Pathophysiology of Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
The underlying pathophysiology of MDS is complex and heterogeneous, and may develop over decades, resulting in progressive dysplasiaGerming U et al. Ann Hematol. 2023;102:311-321. Sekeres MA, Taylor J. JAMA. 2022;328:872-880.
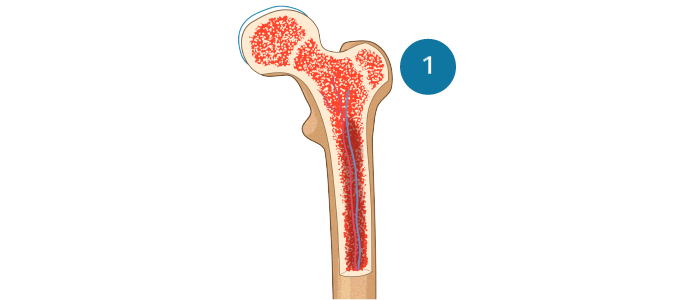
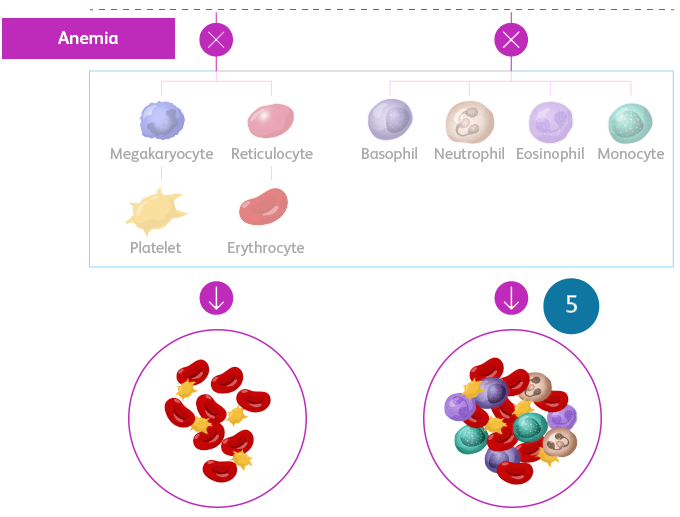
MDS is a spectrum of neoplastic bone marrow failure disorders characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis, resulting in morphologic dysplasia and various degrees of cytopenia.
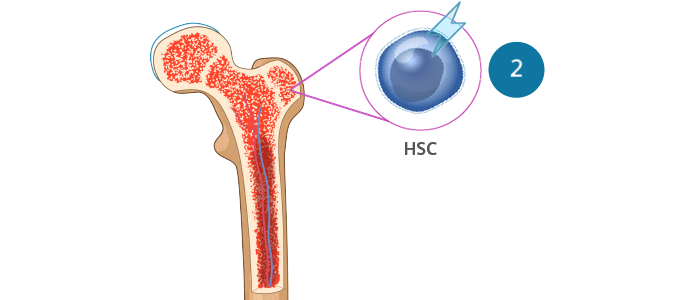
- MDS is a clonal disorder that arises from the expansion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)Sekeres MA, Taylor J. JAMA. 2022;328:872-880. Hoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627.
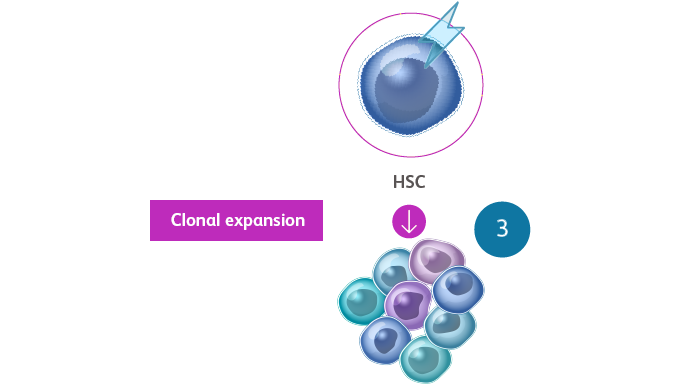
- The somatic mutations that drive MDS confer selective survival advantage over wild-type cells, and the enhanced self-renewal leads to the accumulation of clonal hematopoiesis over time, resulting in abnormal progenitor and precursor cellsSekeres MA, Taylor J. JAMA. 2022;328:872-880. Hoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627.
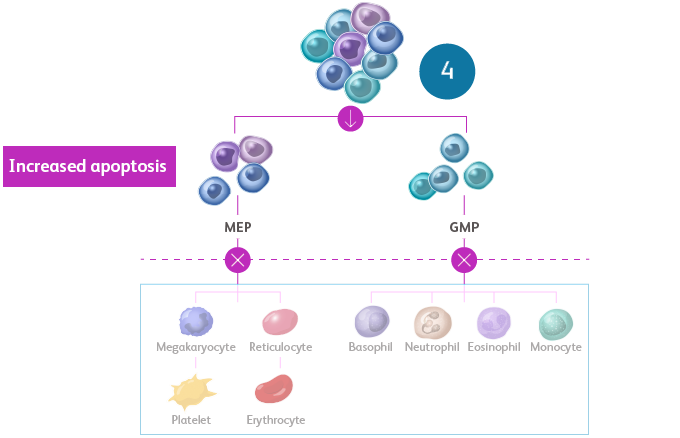
- Terminal maturation is impaired, leading to increased apoptosis of differentiating cells and, thus, peripheral cytopeniasSekeres MA, Taylor J. JAMA. 2022;328:872-880. Hoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627. Sperling AS et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:5-19.
- In 30% of cases, MDS can progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) because of the accumulation of additional mutationsHoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627.
Ineffective hematopoiesis in MDSSekeres MA, Taylor J. JAMA. 2022;328:872-880. Hellström-Lindberg E et al. Haematologica. 2020;105:1765-1779. Adès L et al. Lancet. 2014;383:2239-2252.
Multiple chromosomal abnormalities and genetic mutations have been identified to cause MDSVeiga CB et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:1968.
To learn more, view the tabs below. Each tab contains helpful information.
Most common cytogenetic mutations in MDSHoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627. Saygin C, Godley LA. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:3380.

del, deletion.
- Approximately half of patients with MDS harbor chromosomal abnormalities affecting copy number alteration (eg, deletion, monosomy, or trisomy) or, more rarely, leading to a structural change (eg, balanced translocation or inversion)Hoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627.
- The most common chromosomal abnormality is del(5q), which is present in up to 15% of patientsHoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627.
- Up to 30% of patients with MDS exhibit a complex karyotype (≥ 3 cytogenetic abnormalities), which is associated with a higher risk of progression to AML and a very poor prognosisHoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627.
Landscape of somatic mutations in MDSHoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627. Tobiasson M, Kittang AO. J Intern Med. 2019;286:41-62.
Adapted with permission from J Intern Med.Tobiasson M, Kittang AO. J Intern Med. 2019;286:41-62.
DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; mRNA, messenger RNA; RNA, ribonucleic acid.
- Whole-exome sequencing technologies have enabled detection of recurrent somatic mutations in > 50 genes in up to 90% of MDS casesSaygin C, Godley LA. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:3380.
- Target driver gene mutations are involved in a variety of functional pathways, as shown belowSaygin C, Godley LA. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:3380.
Frequency of driver gene mutations in MDSHoff FW, Madanat YF. Cells. 2023;12:627. Nazha A, eds. Diagnosis and Management of Myelodysplastic Syndromes: A Clinical Guide. Springer; 2020.

Adapted with permission from Springer.Nazha A, eds. Diagnosis and Management of Myelodysplastic Syndromes: A Clinical Guide. Springer; 2020.
Recurrently mutated genes in MDS, categorized according to biological function and mutation frequency. Circle size correlates with mutation frequency; light-colored halos indicate the upper limit of frequency. Mutations that confer an IPSS-R—independent negative effect are colored in blue; mutations with no clear independent effect are displayed as gray/light gray circles. Only SF3B1 mutations are associated with a favorable prognosis (purple).Nazha A, eds. Diagnosis and Management of Myelodysplastic Syndromes: A Clinical Guide. Springer; 2020.
DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; IPSS-R, Revised International Prognostic Scoring System; RNA, ribonucleic acid.