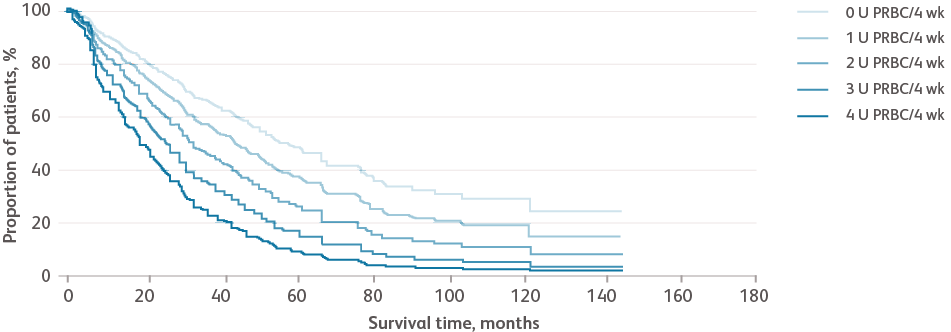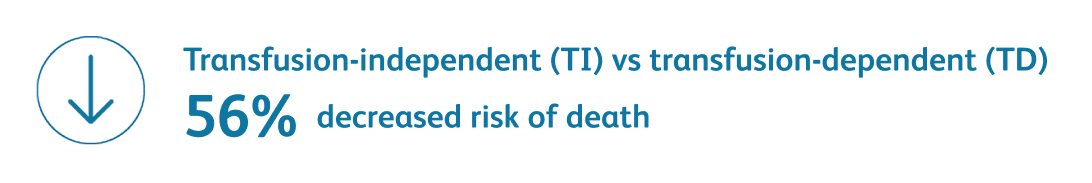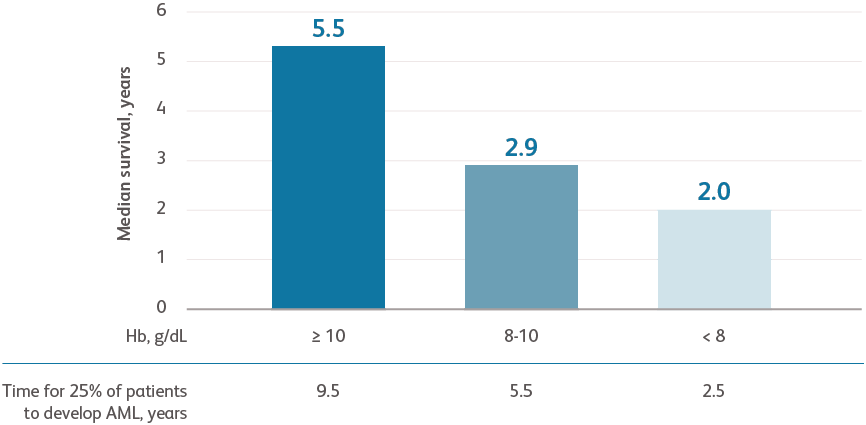
Data are from combined international databases of 7012 patients with primary untreated MDS used to create the IPSS-R.Greenberg PL et al. Blood. 2012;120:2454-2465.
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; Hb, hemoglobin, IPSS-R, Revised International Prognostic Scoring System.
- Severe anemia is associated with a higher prognostic risk, a shorter overall survival (OS), and a more rapid evolution to acute myeloid leukemia (AML)Greenberg PL et al. Blood. 2012;120:2454-2465.
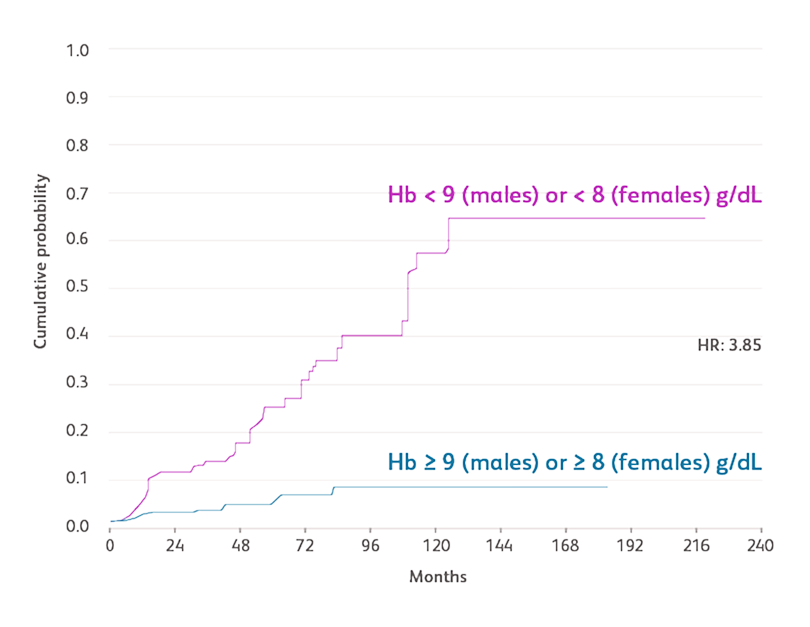
Reproduced with permission from Haematologica.Malcovati L et al. Haematologica. 2011;96:1433-1440.
Data based on a prospective, observational cohort analysis of 840 patients with MDS in Pavia, Italy, and 504 patients with MDS in Düsseldorf, Germany. Cox regression analyses were performed, including age, Hb categories, WHO subgroups, cytogenetic risk groups categorized according to the IPSS, number of cytopenias, and cardiac disease as time-dependent covariates.Malcovati L et al. Haematologica. 2011;96:1433-1440.
Hb, hemoglobin; HR, hazard ratio; IPSS, International Prognostic Scoring System; WHO, World Health Organization.
- Cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, and heart valve disease, were the most frequently observed comorbidities of anemiaMalcovati L et al. Haematologica. 2011;96:1433-1440.
- Males with Hb levels < 9 g/dL and females with Hb levels < 8 g/dL had significantly more frequent cardiac disease and death compared with those with higher Hb levels (incidence rate ratio [IRR]: 1.70 and 4.22, respectively)Malcovati L et al. Haematologica. 2011;96:1433-1440.